Hot-rolled steel is the backbone of modern infrastructure—powering everything from skyscrapers and bridges to heavy machinery and pipelines. Unlike cold-rolled steel, which is processed further for surface finish, hot-rolled steel is prized for its cost-effectiveness, weldability, and mechanical properties.
Choosing the correct grade is not just about fitting a budget; it is critical for ensuring yield strength, ductility, and impact resistance in harsh environments.
Below is a comprehensive guide to hot-rolled steel grades, including naming conventions and equivalence comparisons.

1. Why Grade Selection Matters
Steel is not a "one size fits all" material. The "grade" determines the chemical composition and mechanical properties. Misapplication can lead to catastrophic failures:
●Structural Integrity: Using a low-yield steel (e.g., Q235) where high-tensile loads are expected (requiring Q355/Q460) can cause buckling.
●Weldability: High carbon content increases strength but makes welding difficult (prone to cracking).
●Temperature Resilience: Standard grades may become brittle in freezing temperatures. Grades with specific impact ratings (e.g., J2 or D/E grades) are required for sub-zero environments.
2. Decoding the Naming Conventions
Understanding how these grades are named helps in identifying their properties immediately.
●China (GB/T): Starts with "Q" (Qu Fu -屈服), meaning Yield Strength.
○Example: Q355B = Yield strength of 355 MPa, Quality level B (20°C impact test).
●USA (ASTM): Often arbitrary numbers, though some denote yield.
○Example: A36 = Approximately 36,000 psi yield strength.
●Europe (EN): Starts with "S" (Structural) followed by Yield Strength.
○Example: S355JR = Structural steel, 355 MPa yield, "JR" indicates impact testing at 20°C.
●Japan (JIS): Starts with "SS" (Steel Structure) followed by Tensile Strength (NOT Yield).
○Example: SS400 = Tensile strength of 400 MPa (Yield is typically ~235-245 MPa).
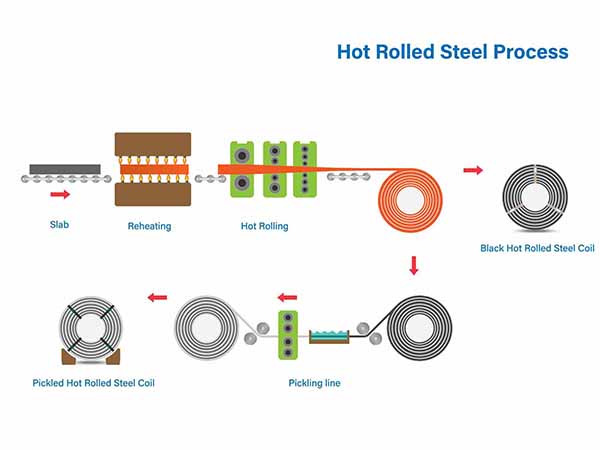
3. Major International Standards & Grades
A. China: GB/T Standards (The Global Manufacturing Hub)
●Carbon Structural Steel:
○Q235 (A/B/C/D): The most common mild steel. Used for general structures, secondary parts, and frames.
●Low-Alloy High-Strength Steel (HSLA):
○Q355 (B/C/D/E): The modern standard for heavy loads (bridges, high-rises).
○Q420, Q460: Ultra-high strength for heavy machinery (cranes, mining trucks).
●Specialty Steel:
○Weathering: Q355NH (Resists atmospheric corrosion).
○Wear-Resistant: NM400, NM500 (Hardened for dump truck bodies, crushers).
B. United States: ASTM & API
●ASTM A36: The standard for mild carbon steel (beams, channels).
●ASTM A572 Gr.50: High-strength low-alloy (HSLA), commonly used where weight reduction is needed without sacrificing strength.
●ASTM A588: "Corten" or weathering steel.
●API 5L (X42–X80): Specifically for oil and gas pipelines. The number (e.g., 42) represents yield strength in ksi.
C. Europe: EN 10025
European grades emphasize impact testing temperatures (Charpy V-Notch):
●S235JR: Standard structural steel.
●S355 (JR/J0/J2/K2):
○JR: Impact test at 20°C.
○J0: Impact test at 0°C.
○J2: Impact test at -20°C (Crucial for cold climates).
D. Japan: JIS G3101
●SS400: The most common general-purpose steel in Asia.
●SM490: "M" stands for Marine/Welded structure, offering better weldability than standard SS grades.
●SPA-H: Superior atmospheric corrosion resistance (widely used in shipping containers).
4. International Equivalent Table (Approximate)
|
Category |
China (GB) |
USA (ASTM) |
Europe (EN) |
Japan (JIS) |
Characteristics |
|
Mild Steel |
Q235B |
A36 |
S235JR |
SS400 |
Good weldability, general construction. |
|
High Strength |
Q355B (formerly Q345) |
A572 Gr.50 |
S355JR |
SM490A |
Higher load bearing, used in bridges/towers. |
|
Weathering |
Q355NH |
A588 |
S355J2W |
SPA-H |
Rusts to form a protective layer. |
|
Pipeline |
L245 / L360 |
API 5L Gr.B / X52 |
L245 / L360 |
— |
Designed for high pressure fluid transport. |
5. How to Choose the Right Grade
When selecting a hot-rolled steel grade, ask these four questions:
1. What is the load?
Light/Static loads:Q235 / A36 / S235.
Heavy/Dynamic loads:Q355 / A572 / S355.
2. What is the environment?
Standard indoor/covered: carbon steel (painted).
Outdoor/Coastal: weathering steel (SPA-H / A588) or Galvanized Q235.
Extreme Cold: choose grades with impact ratings like S355J2 or Q355D/E.
3. Will it be welded?
If heavy welding is required, avoid high-carbon grades. Look for grades denoted "W" (Weathering/Weldable) or low-carbon equivalents like SM490 over SS490.
4. Is wear an issue?
For sliding/impact abrasion (chutes, excavator buckets), structural steel will fail. Use Wear Resistant (NM) series.
Conclusion
Hot-rolled steel covers a wide variety of grades designed for construction, engineering, pipelines, machinery, automotive manufacturing, and industrial applications. Understanding grade systems—GB/T, ASTM, EN, JIS—helps you choose the most suitable material for your project and ensures full compliance with international engineering standards.