Steel sheet piles are a type of steel structure with interlocking devices (lock openings) along the edges. They can be freely combined through the lock openings to form continuous retaining or water-retaining walls and are widely used in temporary or permanent support structures in civil engineering. Its dimensions are usually determined by width, thickness, length and cross-sectional shape. Different models are suitable for the requirements of different projects.
Common types of sheet piles
U-shaped sheet piles: They are the most common type of sheet piles, with a U-shaped cross-section and interlocking openings on both sides, which can interlock with each other to form a continuous retaining wall. The structure is symmetrical, mostly produced by hot-rolling process, easy to use and flexible in construction.
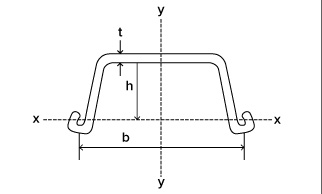
Core advantage
Convenient construction: Suitable for temporary projects such as shallow foundation pits and cofferdams, with fast speed and low cost.
Good waterproof performance: The lock mouth is tight and the water-stopping effect is remarkable (such as the cofferdam of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge).
Economical and environmentally friendly: It can be reused more than 50 times, reducing the amount of concrete used.
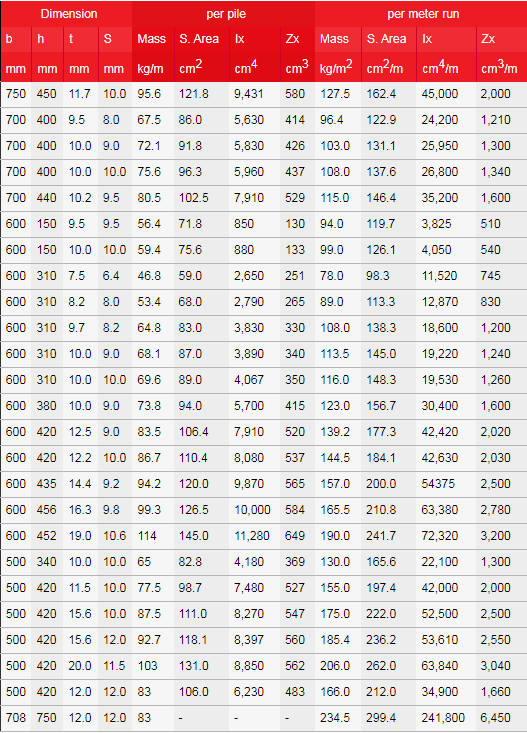
Common specifications
Z-shaped steel sheet piles: The cross-section of Z-shaped steel sheet piles presents a Z shape, and the interlocking openings are symmetrically distributed on both sides of the neutral axis. Compared with U-shaped steel sheet piles, Z-shaped steel sheet piles have higher bending strength and can withstand greater lateral pressure. It is suitable for deep pits and other high-depth scenarios.
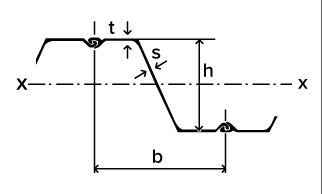
Core advantage
High bending stiffness: The Z-shaped section symmetrically distributes the lock openings on both sides of the neutral axis, and in combination with the continuous web design, significantly increases the section modulus and moment of inertia (30% to 50% higher than U-shaped piles), providing stronger bending resistance. It is suitable for high-stress scenarios such as deep foundation pits and port breakwater.
Cost savings: High material utilization rate, saving 10% to 15% of steel compared to U-shaped piles under the same strength. The construction cost is reduced by 20%.
The lock is precise: It adopts Larssen lock technology, with a tight fit and natural leak-proof effect. No additional water-stopping measures are required, making it particularly suitable for projects with high water tightness requirements such as cofferdams and underground continuous walls.
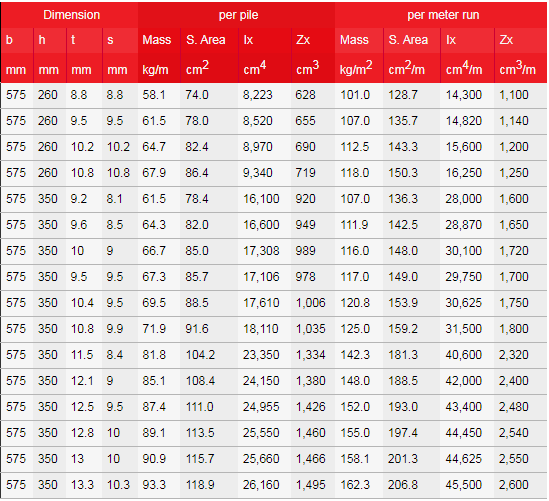
Common specifications
Application scenarios
U-shaped: Temporary support (foundation pit, cofferdam), flood control embankment, small and medium-sized wharf.
Z-type: Deep-water ports, large dry docks, high-load permanent structures (such as the cofferdam of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge).



