The difference between Shipbuilding Steel Plate Grade A Vs B lies in the temperature of the impacting test, as well as the impacting energy value.
Grades: A, B, D, E, AH32/36/40, DH32/36/40, EH32/36/40
According to its yield strength, shipbuilding plate of can be divided into below grades:
Grade A steel is the impact force subjected to normal temperature (20 ° C).
Grade B steel impact force at 0 °C.
Grade D steel impact force at -20 °C.
Grade E steel impact force at -40 °C.
High-strength shipbuilding steel plate can be further divided into: AH32, DH32, EH32; AH36, DH36, EH36 and AH40, DH40, EH40.
1. The general grades A, B, D, and E are distinguished according to the impact temperature of the steel. The impact values of all grades of steel are the same.
2. High-intensity hull structure steel preheating requirements: For all AH, DH, EH plate thickness greater than 30mm angle, butt joints, shall be preheating to 120 ~ 150 °C before welding.
3. For thickness of the plate ≤ 30mm, the ambient temperature is below 5 ° C, preheated to 75 ° C; Ambient temperature below 0 ° C, preheated to 75 ~ 100 ° C.
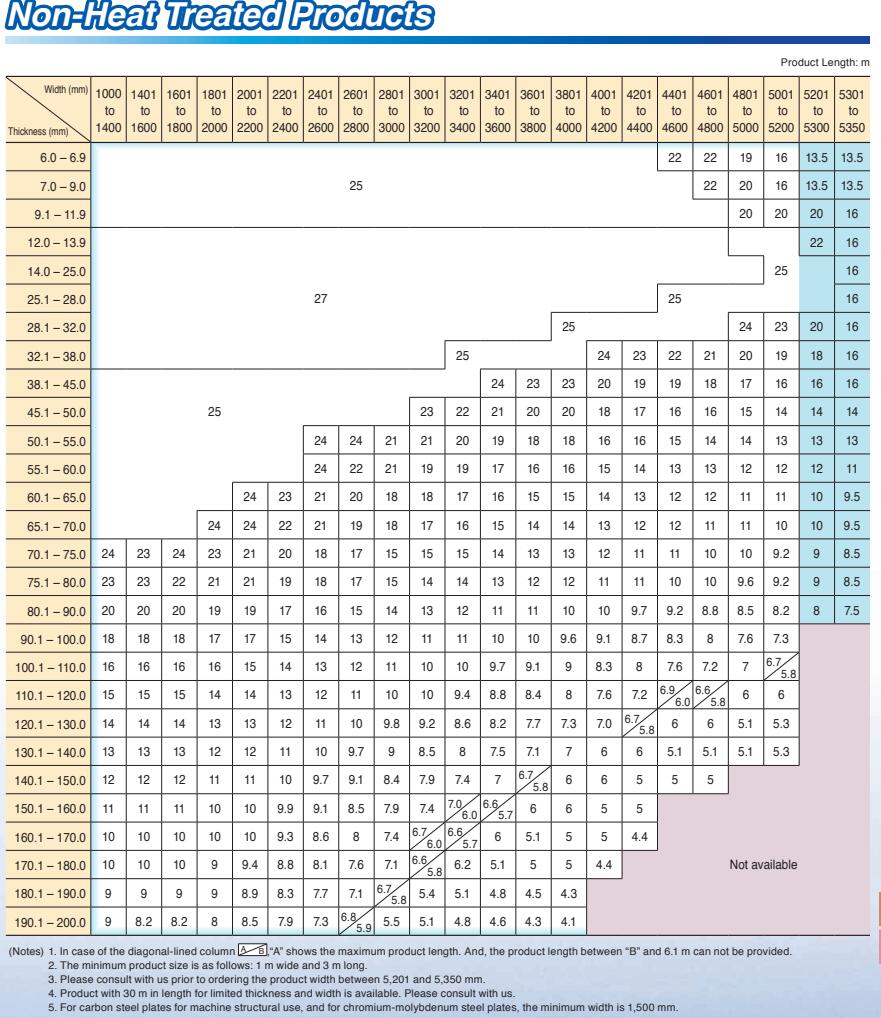
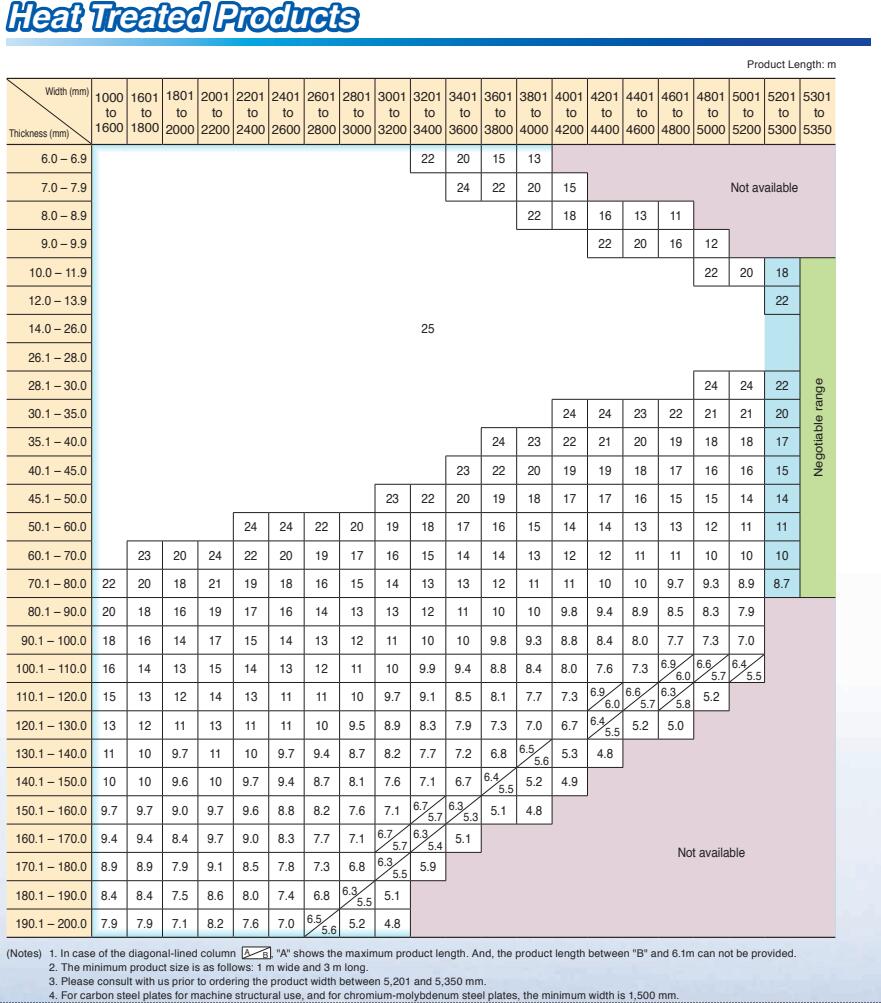
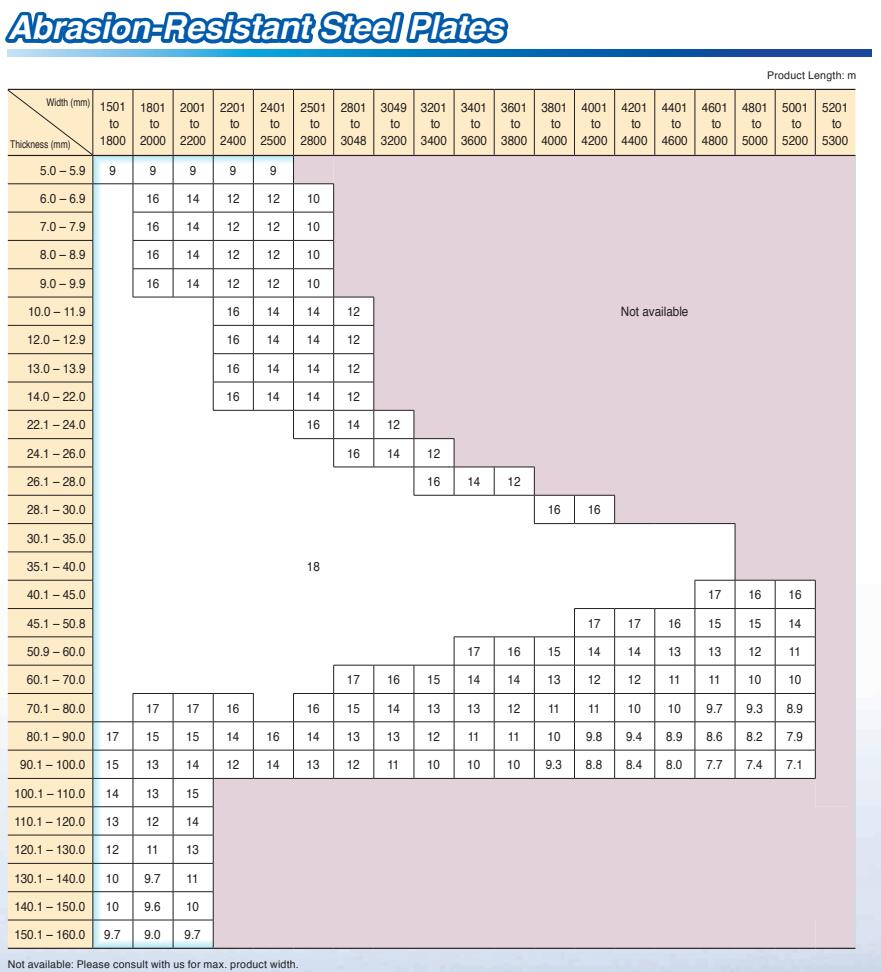
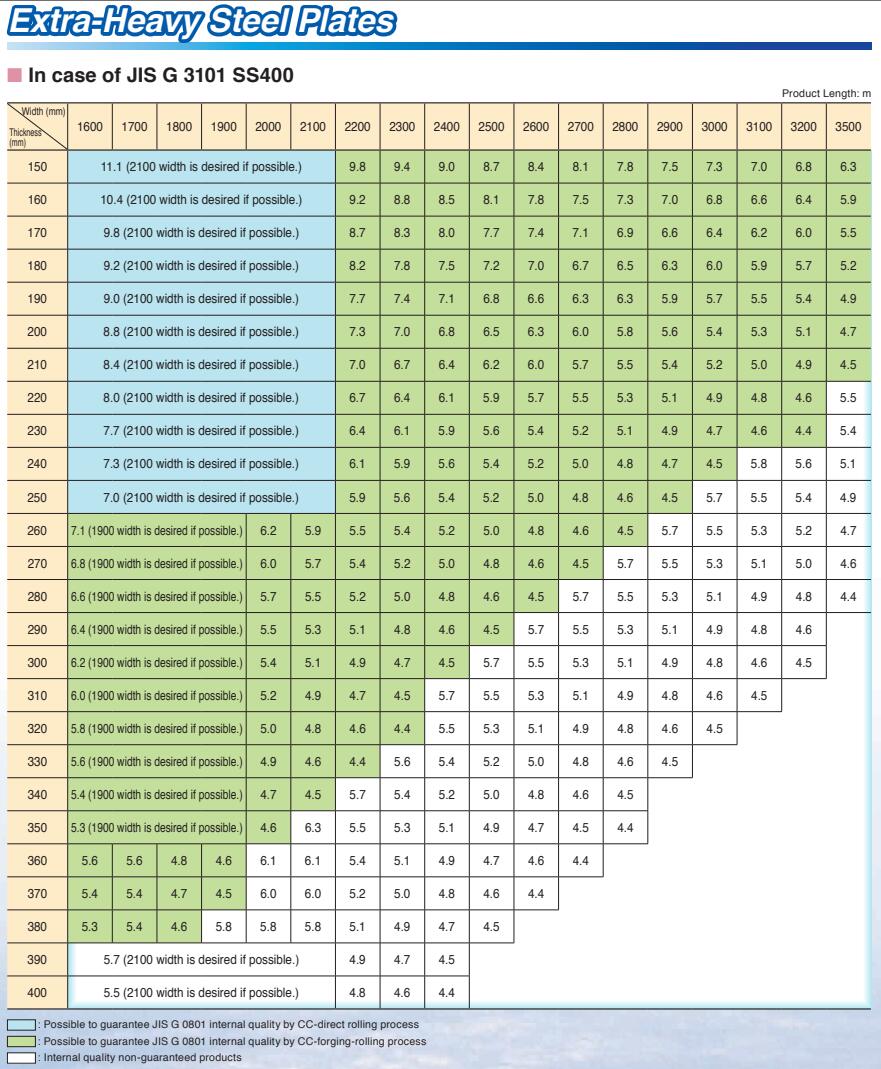
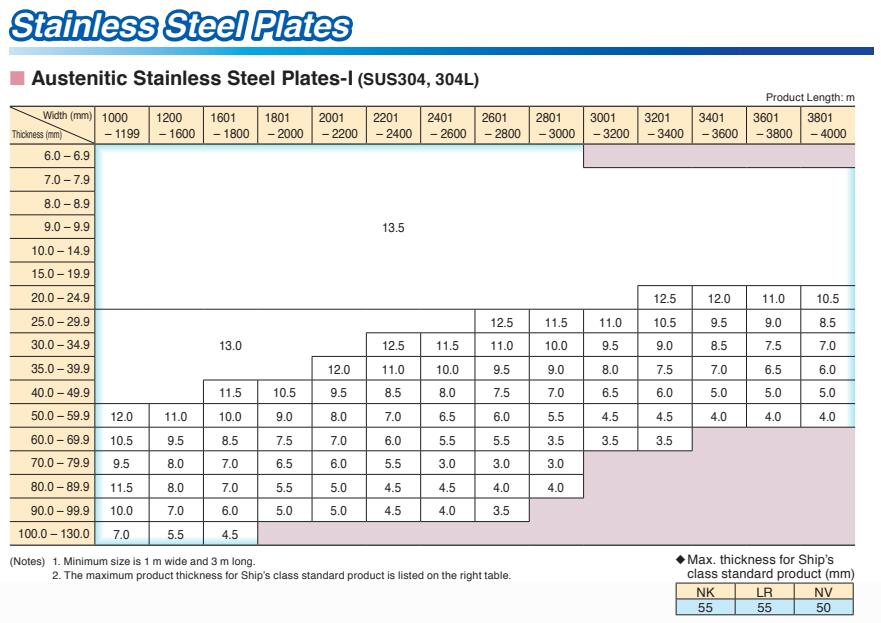
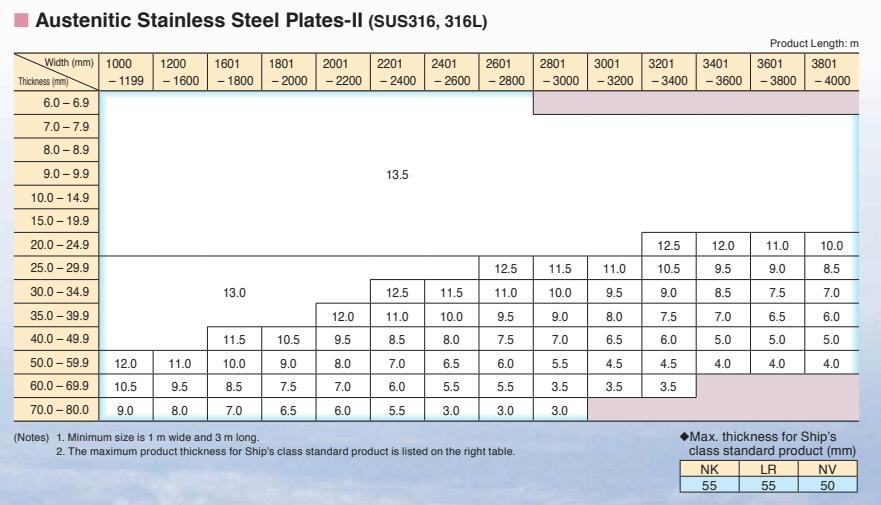
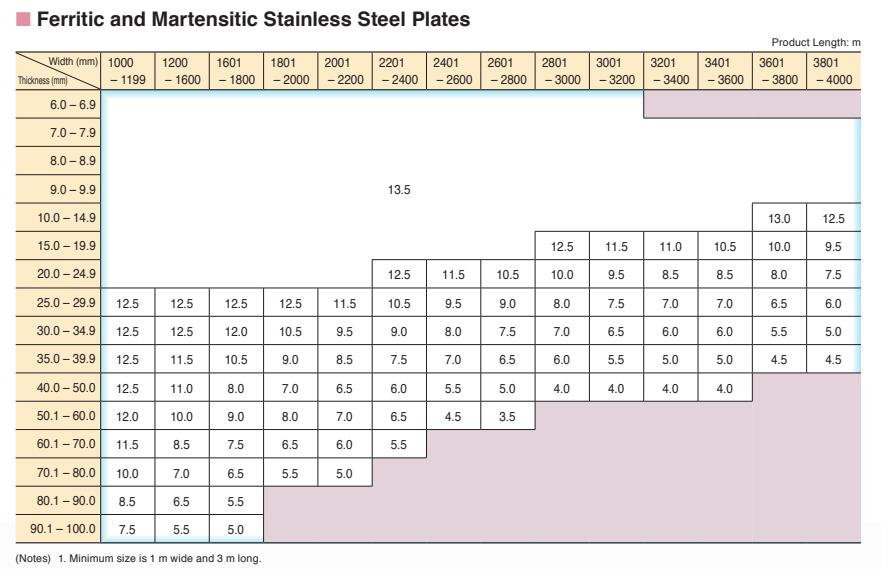
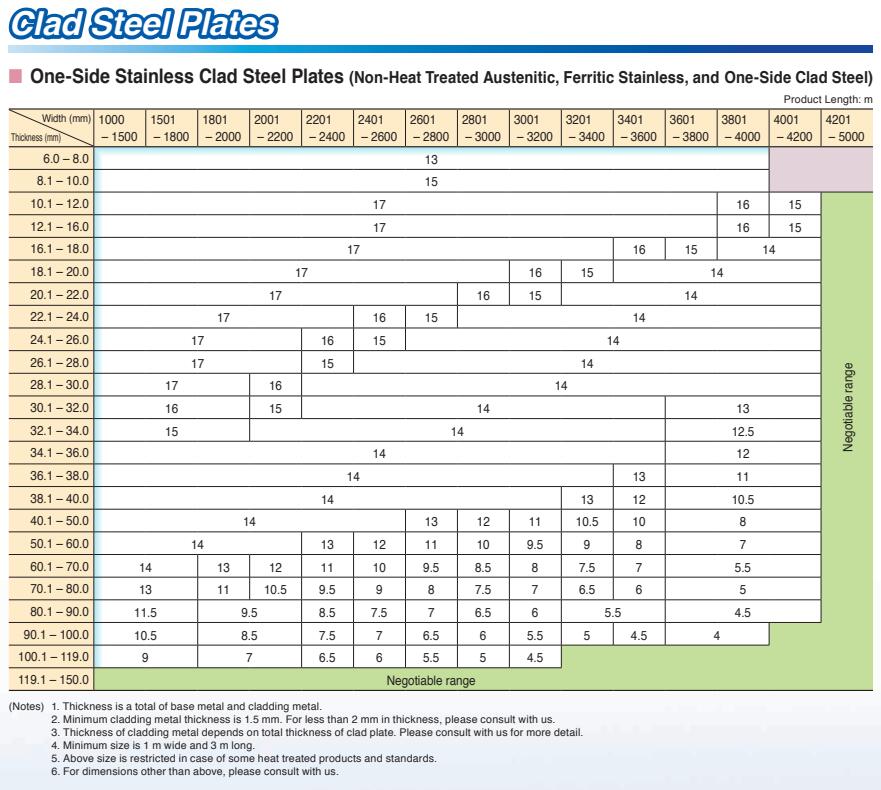
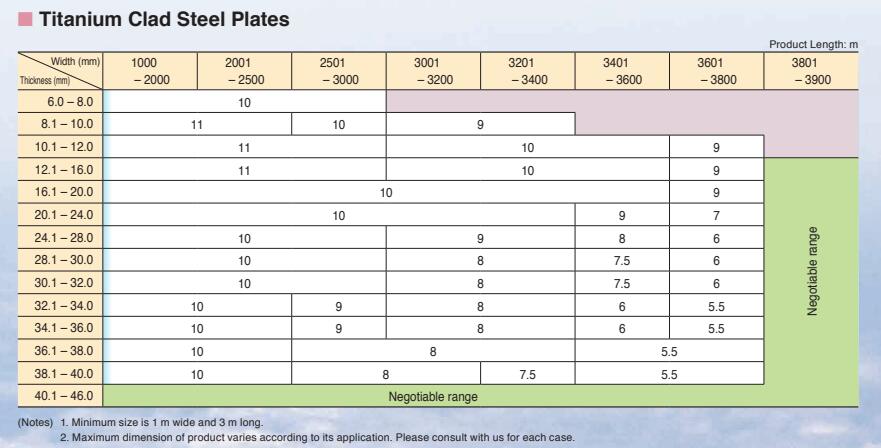
Thickness Range: 5 mm -150 mm
Width Range: 1500 mm - 3900 mm
Length Range: 6 m, 12 m, coils
With anti-rust painting.
|
Elements |
C |
Mn |
Al |
Si |
P |
S |
|
AH32 |
≤0.18 |
0.7~1.60 |
≥0.015 |
0.10~0.50 |
≤0.04 |
≤0.04 |
|
DH32 |
≤0.18 |
0.90~1.60 |
≥0.015 |
0.10~0.50 |
≤0.04 |
≤0.04 |
|
EH32 |
≤0.18 |
0.90~1.60 |
≥0.015 |
0.10~0.50 |
≤0.04 |
≤0.04 |
|
AH36 |
≤0.18 |
0.7~1.60 |
≥0.015 |
0.10~0.50 |
≤0.04 |
≤0.04 |
|
DH36 |
≤0.18 |
0.90~1.60 |
≥0.015 |
0.10~0.50 |
≤0.04 |
≤0.04 |
|
EH36 |
≤0.18 |
0.90~1.60 |
≥0.015 |
0.10~0.50 |
≤0.04 |
≤0.04 |
C (carbon) is an indispensable strengthening element in steel, but the increase in C content reduces the low-temperature impact toughness of steel and deteriorates the weldability of steel. Therefore, it is necessary to control the C content in the steel.
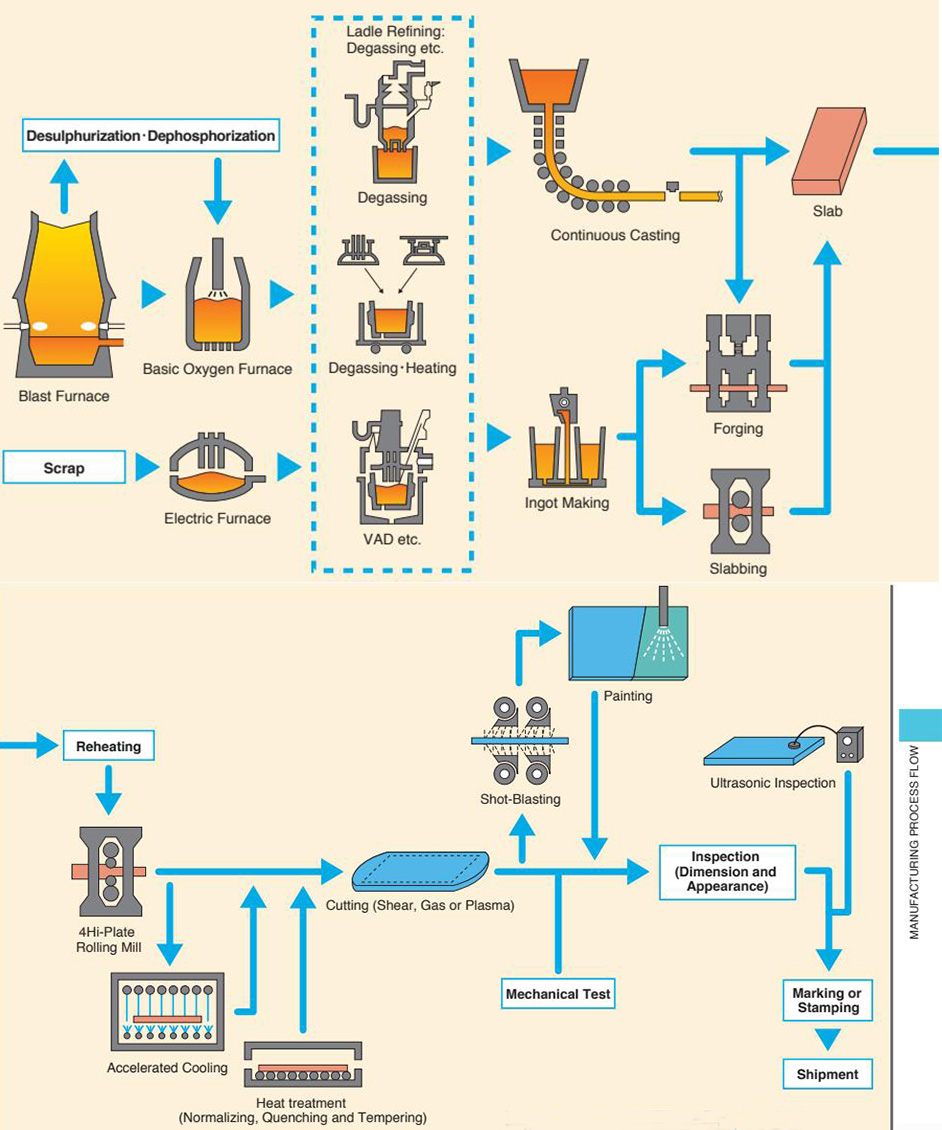
According to the experience of producing aluminsum-containing steel, in order to ensure the aluminum content in the steel and the fluidity of the molten steel, the method of pre-deoxidation is strictly to control the carbon content of the end point and the alloying of the large-pack alloy to control the oxidation of the molten steel. The way of adding aluminum.
In order to ensure good low temperature impact toughness of the steel grade, the rolling of the 355MPa class ship plate adopts a strict type II controlled rolling process.
| Mechanical Properties | |||||||
|
Steel Grade |
Thickness/mm
|
Yield point/ MPa |
Tensile strength/ MPa |
Elongation/ % |
V-type impact test |
||
|
Temperature/ ℃ |
Average impact absorption workAkv/J |
||||||
|
Vertical |
Horizontal |
||||||
|
A |
≤50 |
≥235 |
400~490 |
≥22 |
- |
- |
- |
|
B |
≤50 |
≥235 |
400~490 |
≥22 |
0 |
≥27 |
≥20 |
|
D |
≤50 |
≥235 |
400~490 |
≥22 |
-10 |
≥27 |
≥20 |
|
E |
≤50 |
≥235 |
400~490 |
≥22 |
-40 |
≥27 |
≥20 |
|
AH32 |
≤50 |
≥315 |
440~590 |
≥22 |
0 |
≥31 |
≥22 |
|
DH32 |
≤50 |
≥315 |
440~590 |
≥22 |
-20 |
≥31 |
≥22 |
|
EH32 |
≤50 |
≥315 |
440~590 |
≥22 |
-40 |
≥31 |
≥22 |
|
AH36 |
≤50 |
≥355 |
490~620 |
≥22 |
0 |
≥34 |
≥24 |
|
DH36 |
≤50 |
≥355 |
490~620 |
≥22 |
-20 |
≥34 |
≥24 |
|
EH36 |
≤50 |
≥355 |
490~620 |
≥22 |
-40 |
≥34 |
≥24 |